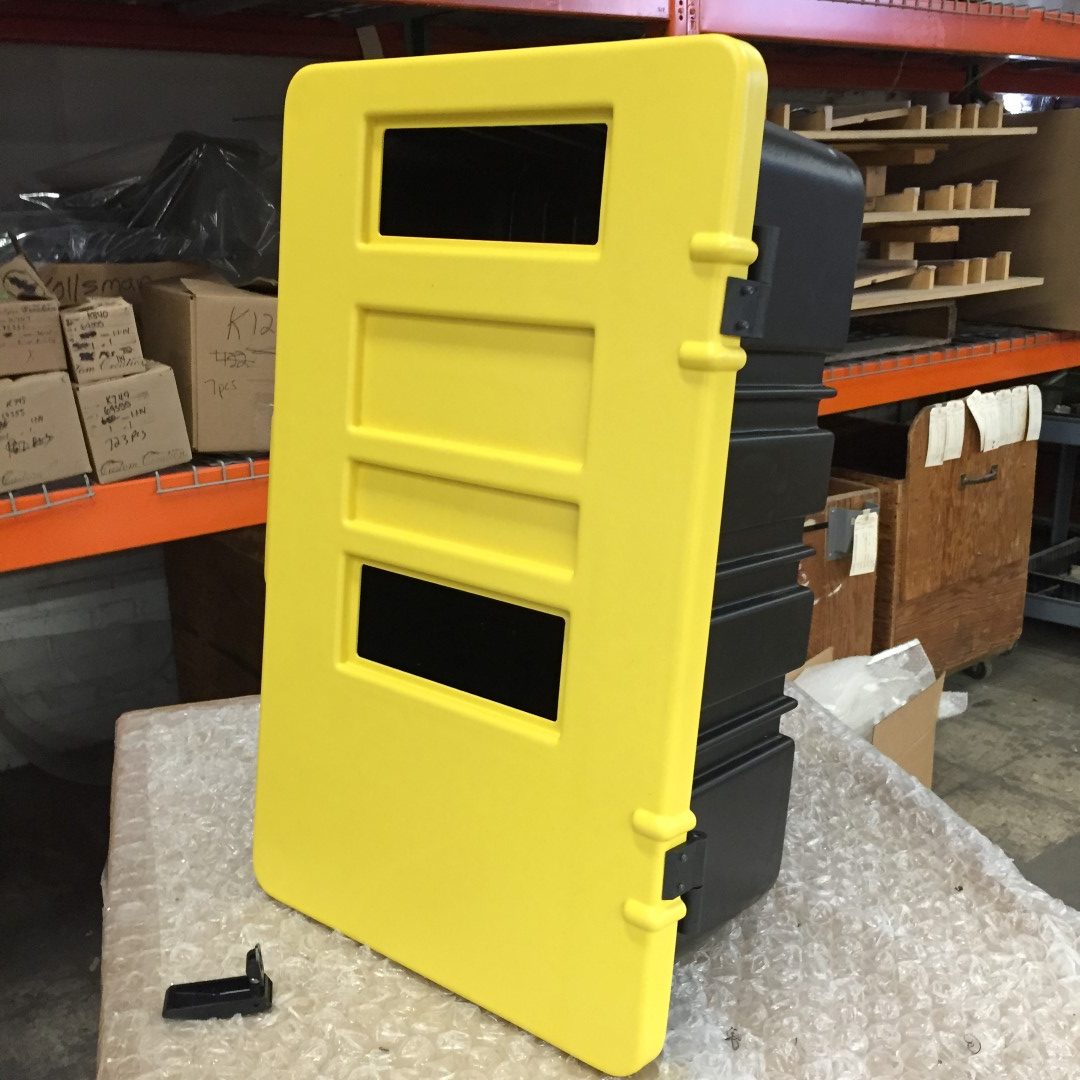
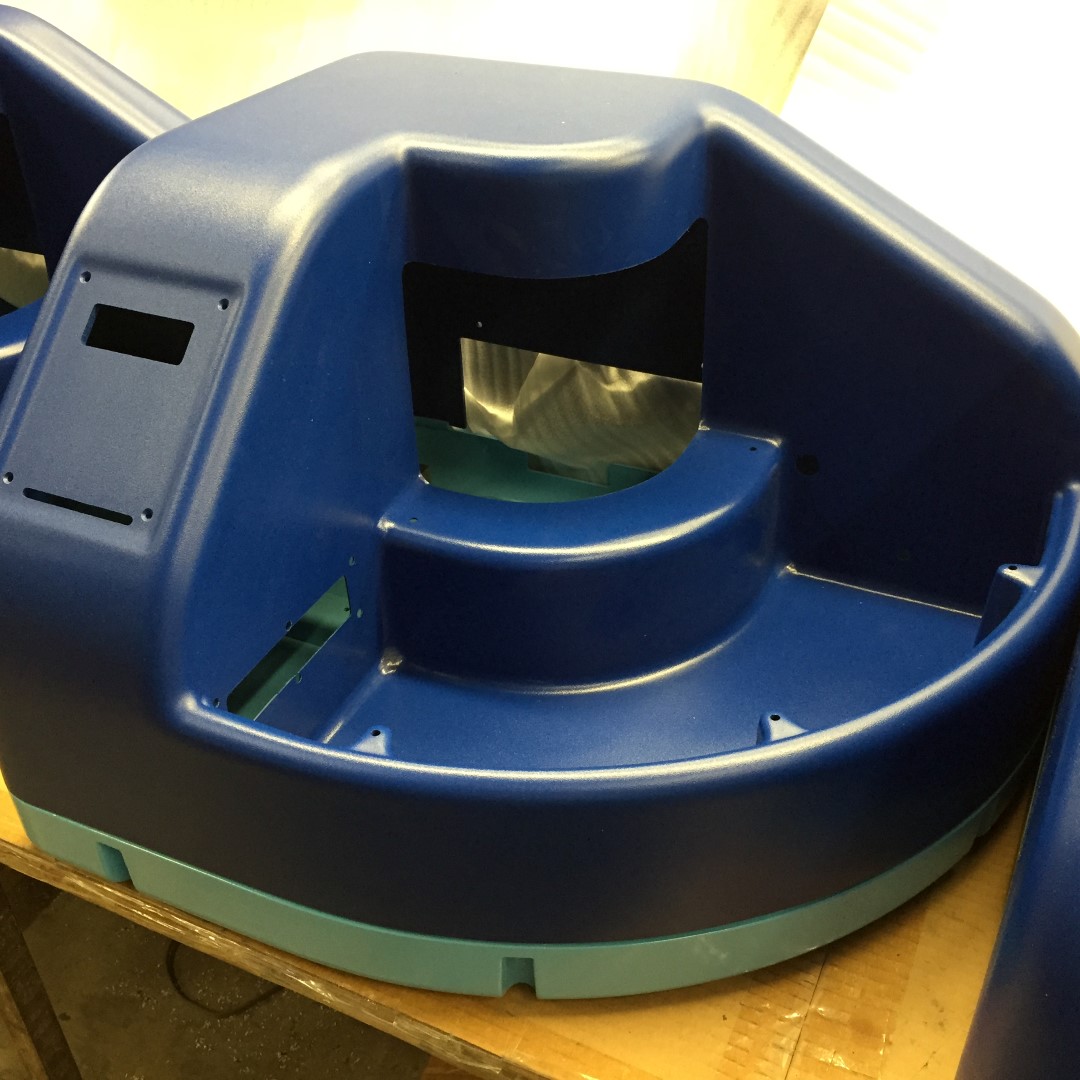
Thermoforming
Transform Your Ideas
The thermoforming process consists of the heating of a plastic sheet, which is then draped over a mold while a vacuum is applied. The molding is then cooled before it is ejected using reverse pressure. Thermoforming is an economic, fast, and fantastic alternative to traditional injection molding for smaller production runs.
Vacuum forming is one of the most widely-used methods of thermoforming, a common alternative to injection molding. It’s a truly cost-effective process perfect for producing low volume, large sized parts at a price that makes sense. The advantages of vacuum forming as an alternative to injection molding is the ability to form large parts without costly equipment and tooling, low cost mold and design revisions, ease of manufacturing large quantities, and the ability to create padded foam filled or laminated parts.
Here’s how it works: A male or female mold tool is mounted in a machine and a heated sheet is located over or under the tool. The vacuum is then applied to remove the air between the sheet and the mold. The vacuum is used to transfer the heated sheet into contact with the mold surface. The atmospheric pressure holds the sheet until the temperature decreases below its heat distortion temperature.
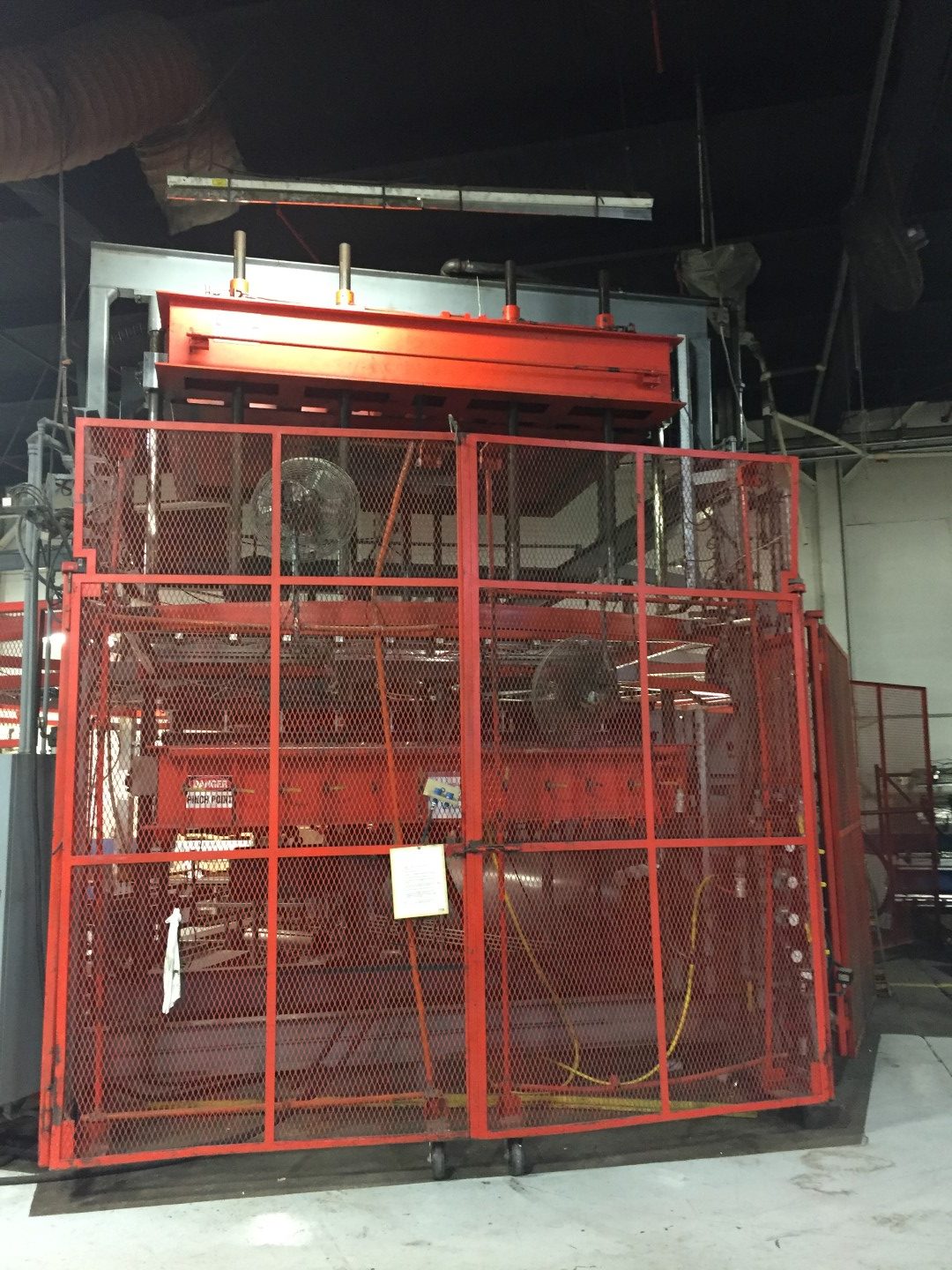

There are many types of services that CW Thomas offers, including acrylic, ABS, and PVC thermoforming. Pressure forming gives you injection-mold quality, high definition plastic component parts, housings and containers – but without the huge expense of tooling. It involves positive pressure to force the heated plastic into the mold cavity. This is called pressure thermoforming or blow forming. Some of the advantages of pressure forming are:
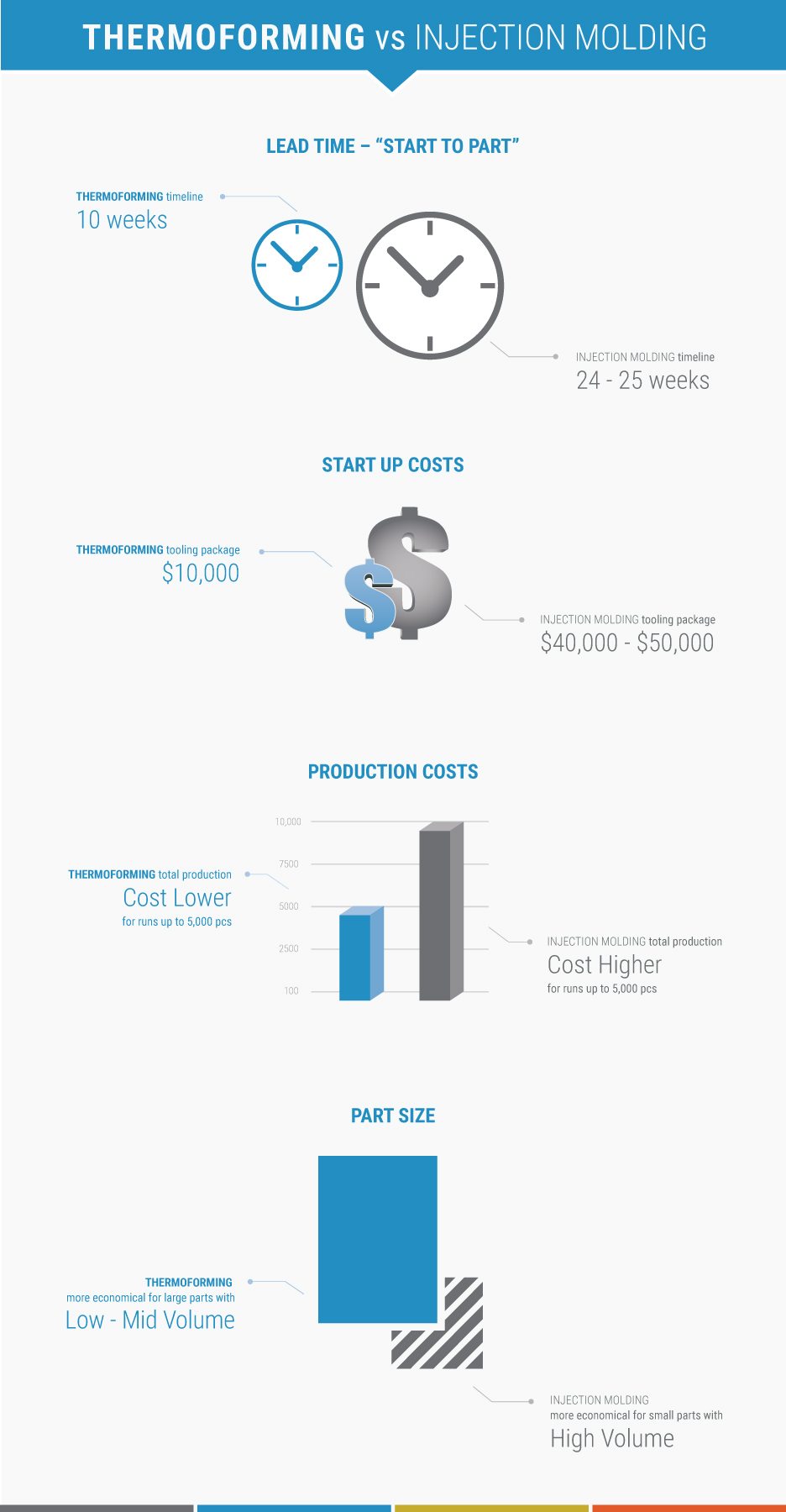
- Lower tooling cost and faster turnaround times make thermoforming a great alternative to injection molding
- High cosmetic features such as sharp detail and tight corner radii are required, optical aesthetics
- Process of choice when deep drafts or undercuts are required
- Embossed logos, design features, vents, etc. can be incorporated into the design
- Mold texture or painted finishing (unlimited options)
- Higher impact strength requirements compared to injection-molded parts due to no molding weld lines
- Short (from 10pcs/year) to medium (up to 5000pcs/year) run requirements
- Ideal for functional market-sampling trials (prototyping) and shorter life cycle products
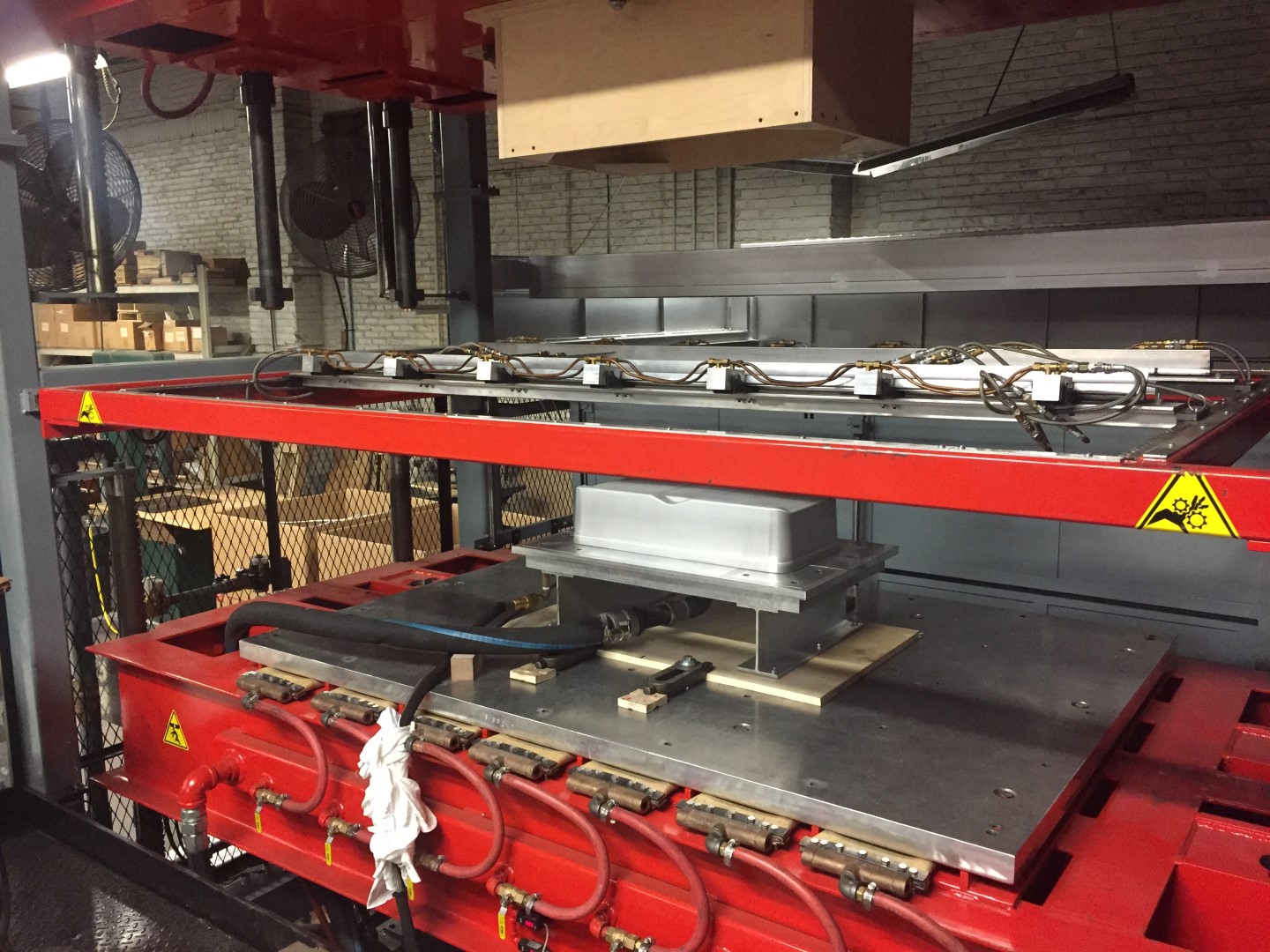

The advantages of thermoforming over injection molding include:
- Lower costs for small to medium production runs
- Lower tooling costs Single sided VRS; Double sided molds
- Less set-up and lead time
- Excellent color and texture forming
- Shorter lead-time to production start
- Secondary CNC work yields features without weak spot weld lines
- Excellent surface finish
- Large part molding
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Very common material. Good stiffness and impact strength. Available in a wide variety of colors and several textures. Available in UL94-V0 grades (Flame Retardant)
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene): Low cost, forms easily. Available in many colors. More brittle than ABS.
HDPE (High Density Polyethylene): Excellent impact and chemical resistance. Good cold temperature properties. Dimensionally not as stable as other materials.
PP (Polypropylene): Excellent chemical resistance. Rigid, with very good impact strength. Good at higher temperatures. But dimensionally not as stable as other materials, similar to HDPE.
TPO (Thermoplastic Polyolefin): Outstanding impact properties. Available with high gloss finish. Good for outdoors applications. More difficult to form, especially deep draw shapes.
ACRYLIC (PMMA – Polymethyl Methacrylate, Plexiglass): Water clear and abrasion resistant material. Easily fabricated. Available in impact modified grades. Many colors available.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Rigid material. Very good impact strength. Flame retardant. Limited availability.
KYDEX (PMMA / PVC blend): Good general-purpose material, offering excellent impact and chemical resistance in a highly cosmetic sheet. Most grades are flame retardant to UL94-V0, and meet air, rail, and vehicle flame smoke and toxicity requirements. Available in many colors and textures.
Boltaron (PVC/ABS): Very similar to Kydex. Extreme formability with uniform wall thickness, excellent impact and chemical resistance. Most grades meet MVSS Docket 90 and 90A, UL 94 V-0 and 5V, Class 1-A fire ratings. Available in many colors including solids, translucents, and metallics.
PC (Polycarbonate): Very high impact strength. Clear. High temperature resistance.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Clear, with excellent impact strength. Forms well.
PEI (Polyetherimide, Ultem): Very high temperature grade material. Autoclavable. Natural amber color.
PPSU (RADEL): High temperature grade material, autoclavable, high strength.